
Key Shipping and Logistics Trends | September 2024 Market Outlook
Global Schedule Reliability Declines
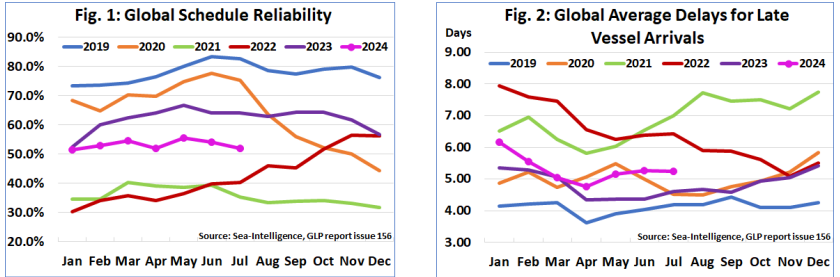
Global shipping schedule reliability saw a 2.1 percentage point drop in July, pointing to ongoing challenges across supply chains. Several factors are contributing to this decline, including increased congestion at major ports, inefficiencies in operations, and unexpected weather-related disruptions. These challenges are part of a larger, industry-wide trend affecting shipping schedules globally.
Industry Implications
This decline in reliability poses serious risks for businesses, including higher costs, inventory shortages, and unpredictable delivery times. To address these challenges, companies should enhance their contingency planning and communication strategies. Although the situation may stabilize, a return to pre-disruption levels of reliability is unlikely in the short term, requiring ongoing adjustments in logistics operations.
Latest Ocean Freight Market Shifts – September 2024
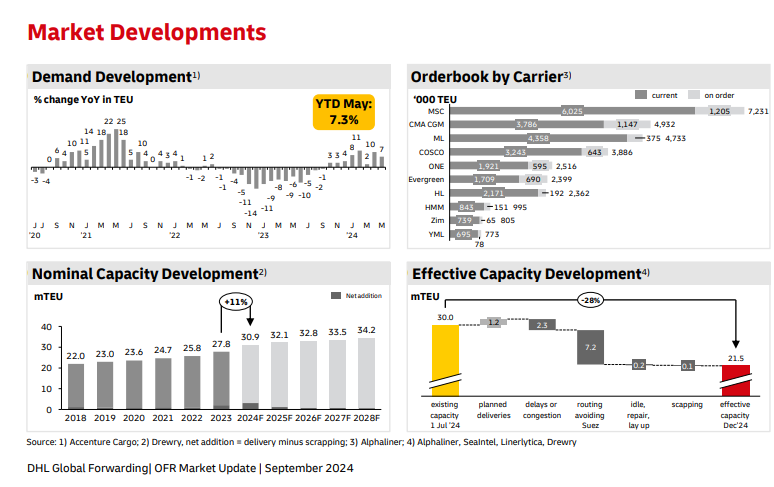
Key | |
++ | Strong Increase |
+ | Moderate Increase |
= | No Change |
– | Moderate Decline |
— | Strong Decline |
Outbound
Middle East – Asia
The capacity between the Middle East and Asia remains stable, with no significant changes reported in this period. Rates have seen a moderate increase, reflecting heightened demand or reduced competitive offerings.
Capacity — (=)
Rate – (+)
Middle East – Europe
There has been a strong decline in capacity, possibly due to strategic reallocations or disruptions in service routes. Rates have strongly increased, likely a response to reduced capacity and sustained or growing demand.
Capacity – (-)
Rate — (+)
Middle East – Latin America
Capacity to Latin America is under pressure, with tight space and full vessels contributing to delays. Rates for inbound shipments are increasing due to strong demand and limited capacity.
Capacity – (-)
Rate — (+)
Middle East – North America
The capacity to North America is also constrained due to increased volumes and vessel space limitations. Rates are rising as Peak Season Surcharges come into effect amid strong demand.
Capacity – (-)
Rate — (+)
Inbound Updates
Asia – Middle East
The capacity remains robust, with strong export volumes from China and other Asian markets, particularly driven by Far East Asia and Intra-Asia trade. Rates are moderately increasing due to continued strong demand for exports and increased air freight volumes.
Capacity — (+)
Rate — (+)
Latin America – Middle East
Capacity is moderately declining due to high demand and limited vessel availability. Rates are seeing a moderate increase, driven by strong demand and the introduction of Peak Season Surcharges (PSS).
Capacity — (-)
Rate — (+)
North America – Middle East
Continued disruptions and potential strikes are leading to service inconsistencies. Rates are moderately increasing, driven by high demand and Peak Season Surcharges (PSS).
Capacity — (-)
Rate — (+)
Europe – Middle East
The capacity remains tight due to high demand and supply chain disruptions.
Capacity — (-)
Rate — (+)
Monthly Air Freight Update | Developments for September 2024
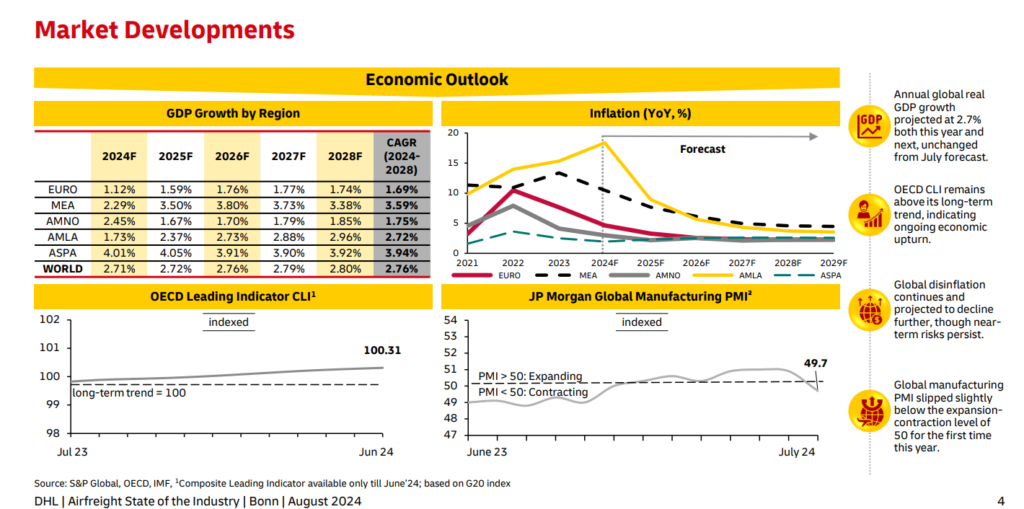
Demand: The air cargo demand continues to rise because of the ecommerce growth, disruptions in ocean freight, and increasing general cargo needs for high-tech semi-conductors. This growth in demand is expected to be carried on throughout 2025 and beyond, despite the mixed economic signals.
Capacity: The capacity for air freight is expected to remain tight in H2’ 2024 after an increase in the demand for ecommerce and geopolitical tensions. Furthermore, the deliveries for widebody aircraft have slowed down amid supply chain issues and conversion constraints.
Rates: The air cargo rates have defied seasonal trends by hitting the highest level of the year because of the supply-demand imbalance. The air cargo industry is anticipating peak holiday season demand, expecting elevated rates and capacity pressure.
The Middle East and Air Carriers
There is a strong sea-air demand from Dubai, while Oman is being used as an additional alternate hub. The rates from the UAE to EU are expected to rise in the peak season due to the export demand in Asia Pacific.
Asia
In Asia Pacific, there is a predicted strong peak season because of the rising demand and high uptake of fixed capacity, which has driven the cargo rates. The capacity constraints are observed across all AP markets including gateway for transshipments. However, the integrators have announced their plans for peak season surcharge in Q4 2024 to tackle limited capacity and difficulty in securing additional space during year-end period.
America
Transpacific Eastbound is seeing increasing demand and rates as the capacity is relatively stable before a strong peak season. In North America, the US transatlantic cargo is declining for both imports and exports. The exports to Asia Pacific remain weak; however, the import tonnage is increasing YoY and expected to keep rising for the rest of the season. Lastly, MX faces constraints to BR, AR, PE, and CL, which is causing cargo backlogs and rising rates.
Europe
Several carriers are shifting the existing capacity to the NE Asia to Europe corridor during peak season, resulting in reduced capacity on other trade lanes. Furthermore, there is a strong air freight demand inbound Europe, especially from Asia, which is expected to remain for the rest of the year.
UAE Shipping Sector Insights | September 2024 Review
Hapag-Lloyd has updated its website with new geographical fee sections for cargo planning, including changes by country. Read more for details
Maersk is streamlining its communication channels by merging its UAE export business operations into a single address to enhance customer service efficiency. For more details, visit here.
CMA CGM encourages customers to subscribe to their UAE local websites in Dubai and Abu Dhabi to access centralized information, daily vessel schedule updates, and essential advisories. Subscribe for Dubai and Abu Dhabi.
Maersk now allows consignees and related parties to purchase free time extensions online for import shipments in the UAE before container discharge. For detailed information visit this link.
Global Factory Output – Overview
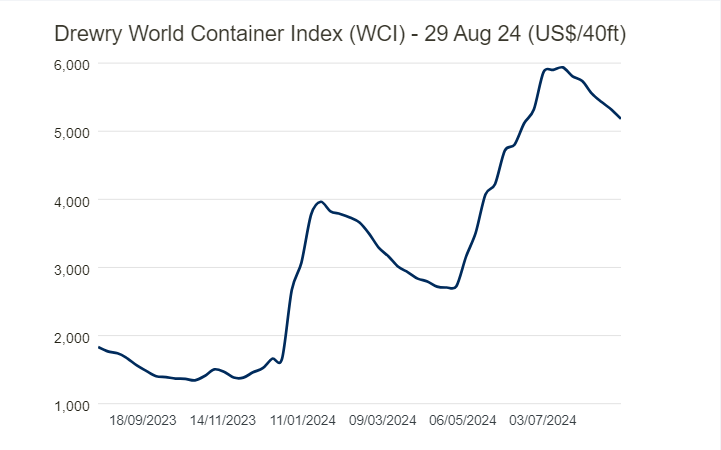
Drewry’s World Container Index has reduced by 3% to reach $5,181 per 40ft container.
United States of America (USA)
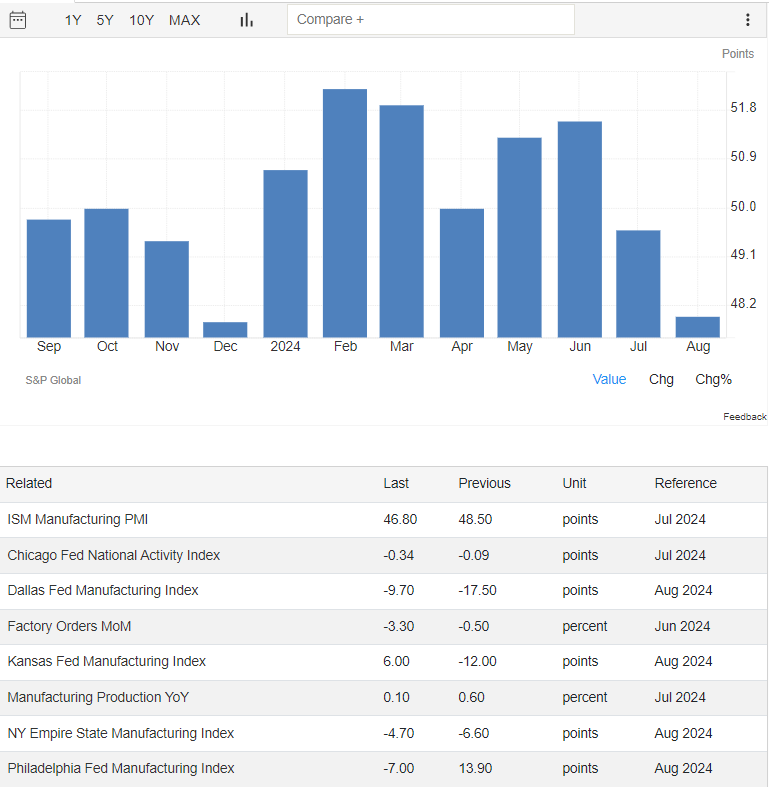
In August 2024, the US Manufacturing PMI fell to 48, marking a sharp contraction in factory activity due to declining new work inflows, affected by high interest rates. Employment growth slowed to its lowest point since January, and reduced factory demand improved raw material delivery times. Input costs rose significantly, but manufacturers could not fully pass these increases to consumers.
United Kingdom (UK)
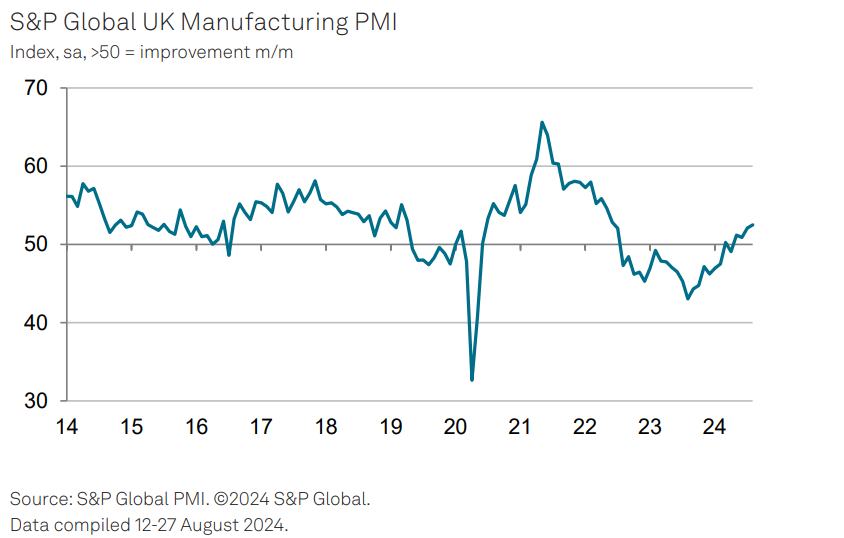
In August, the UK manufacturing sector experienced notable growth, with the PMI reaching a 26-month high of 52.5, driven by strong domestic demand. However, the sector faces challenges in exporting due to reduced demand from Europe and China, high shipping costs, and other global issues. These challenges are causing supply chain disruptions and pushing up manufacturing input costs significantly.
China
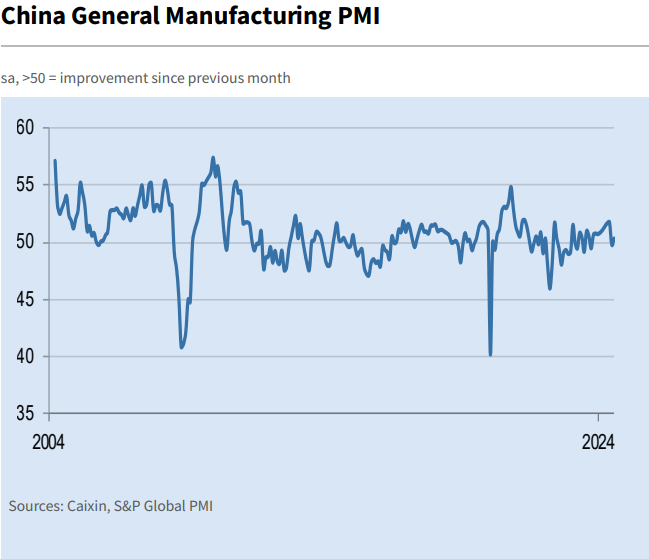
In the third quarter of 2024, China’s manufacturing sector improved with the PMI rising to 50.4, indicating growth driven by new orders and faster production. Employment stabilized, and inventory levels increased. Export orders declined slightly, and supply issues caused vendor performance to worsen. However, input costs fell, prompting manufacturers to reduce selling prices. Overall, confidence in the sector reached a three-month high due to optimistic business development expectations.
United Arab Emirates (UAE)
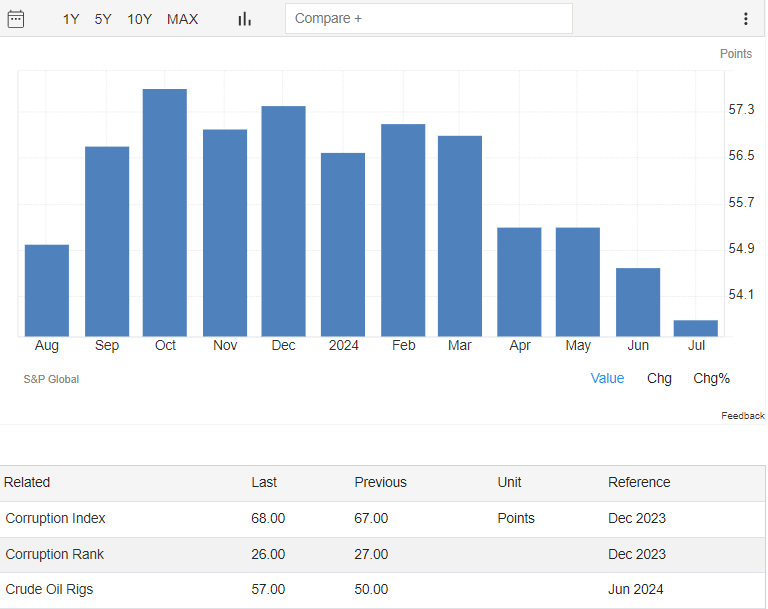
In July 2024, the UAE’s PMI dropped to 53.7, the lowest since September 2021, with output and new business growth slowing amidst strong competition. Although delivery times improved and input purchases increased, job creation hit a six-month low, and firms faced rising work backlogs, leading to a decrease in inventories for the first time since November 2020. Rising material costs pushed inflation to a two-year high, prompting firms to increase output charges. Despite these challenges, companies are cautiously optimistic about the economic outlook, though confidence has weakened to its lowest since January.
Related Articles
March 2025 Global Trade & Logistics Market Update
Ramadan 2025: Road Restrictions and Their Impact on Logistics in Abu Dhabi With Ramadan 2025 approac
Monthly Update on the Global Logistics Market – February 2025
Major Shifts in Carrier Alliances Reshape Global Shipping Dynamics 2025 marks a pivotal year in the
January 2025 Supply Chain and Logistics Industry Outlook
Supply Chain Trends to Watch in 2025 In 2025, the supply chain industry is set to undergo significan







Post a comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.