
Monthly Update on the Global Logistics Market – February 2025
Major Shifts in Carrier Alliances Reshape Global Shipping Dynamics
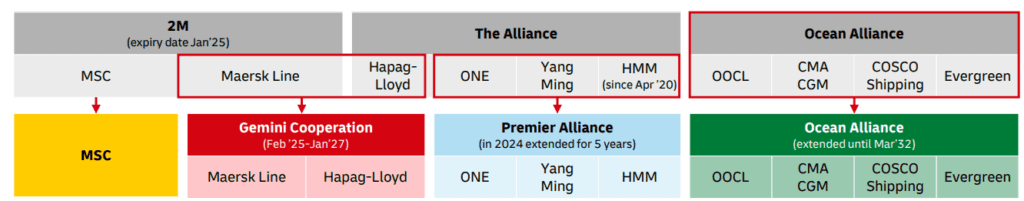
2025 marks a pivotal year in the global shipping industry as major carrier alliances undergo significant reshuffling, impacting service routes, capacity management, and overall maritime logistics. These changes promise to redefine trade lane operations and competitive dynamics among the leading shipping companies.
Details of the Alliance Changes
2M Alliance Breaks Up
As of January 2025, the 2M alliance, previously consisting of MSC and Maersk, will dissolve, leading each carrier to pursue independent strategies in the East-West network. This split is anticipated to affect their service offerings and operational efficiencies.
Introduction of Gemini Cooperation
Commencing in February 2025, the new ‘Gemini Cooperation’ will see Maersk and Hapag-Lloyd collaborating until January 2027. This partnership is expected to focus on improving service reliability and network coverage, utilizing a ‘hub and spoke’ model to enhance direct port calls and manage capacities more effectively.
Formation of Premier Alliance
In response to shifting market demands and the departure of Hapag-Lloyd, THE Alliance members HMM, ONE, and Yang Ming will expand their collaboration under the newly formed Premier Alliance starting February 2025. This alliance aims to consolidate their services and optimize their operational capabilities across crucial trade lanes.
Extended Collaboration in Ocean Alliance
The Ocean Alliance, comprising CMA CGM, COSCO Shipping, OOCL, and Evergreen, extended its cooperation until March 2032. This long-term commitment is set to stabilize their presence in the market and ensure consistent service amidst the volatile shipping landscape.
Impact on Global Shipping
These strategic realignments among the top carriers are expected to significantly influence global shipping routes, capacity allocations, and rate dynamics. Shippers need to stay informed about these developments, as they could affect transit times, service availability, and cost structures. The restructuring could also lead to improved efficiencies and more tailored services to meet regional demands.
February 2025 Global Ocean Freight Review
Key | |
++ | Strong Increase |
+ | Moderate Increase |
= | No Change |
– | Moderate Decline |
— | Strong Decline |
Outbound
Middle East – Asia
The trade lane from the Middle East to Asia consistently shows demand exceeding capacity from January to April 2025.
Capacity – (-)
Rate – (+)
Middle East – Europe
Persistent blank sailings primarily in the Eastern Mediterranean impact shipment schedules.
Capacity – (-)
Rate – (=/ +)
Inbound
Asia – Middle East
The trade lane from Asia to the Middle East shows a transition from balanced demand and capacity to demand exceeding capacity from January to April 2025.
Capacity: (-)
Rate: (+)
North America – Middle East
Service instability and tight vessel space are increasing monthly rates.
Capacity – (-)
Rate – (+)
Europe – Middle East
The trade between Europe and the Middle East shows balanced demand and capacity from January to April 2025.
Capacity – (=)
Rate – (=)
Air Freight Market Insights for February 2025

Demand: Global air cargo demand stayed strong in late 2024, led by AP and AMNO carriers, with e-commerce as a key growth driver. Demand from AP softened in early January but is rebounding as shippers accelerate deliveries for the Lunar New Year.
Capacity: In January 2025, global air cargo capacity increased by 6% year-over-year, led by growth on the AP-AMLA route, with e-commerce driving high-capacity utilization.
The Middle East and Air Carriers
In late 2024, Middle East exports remained robust, fueled by persistent demand for sea-air cargo solutions, which kept airfreight rates elevated. Despite the Gaza ceasefire, the ongoing threats to Red Sea shipping routes have not altered threat assessments, suggesting that both air cargo rates and demand from the Middle East and Africa (MEA) region will remain high into the foreseeable future. This continued tension underscores the critical role air cargo plays in regional trade under complex geopolitical situations.
Asia
Despite looming US tariff threats and increased cargo scrutiny, Asia’s e-commerce sector is poised for continued growth in 2025. However, the overall air cargo supply and demand are expected to face challenges due to a lack of capacity additions. This scenario suggests a strained but growing market, as demand outpaces available air cargo space, potentially impacting delivery times and costs.
America
During the January to November 2024 period, air trade from the Americas North (AMNO) to Europe experienced a 4% decline compared to 2023, primarily due to reduced US exports of industrial materials and machinery parts. Concurrently, the increase in indirect freighter capacity into Mexico via Anchorage highlights Mexico’s strategic importance in nearshoring efforts, emphasizing its pivotal role in reconfiguring supply chains to enhance proximity and responsiveness.
Europe
In 2024, European main hubs experienced a notable increase in air cargo volumes, with Vienna achieving a record-setting 22% growth. This surge reflects robust trade flows, particularly between Asia-Pacific and Europe, which saw a significant 20% year-over-year increase in inbound volume compared to 2023.
UAE Shipping Sector Updates – February 2025
DP World introduces new haulier nomination and token process on Dubai Trade portal. Read More
CMA CGM revamps AMERIGO service between the Mediterranean and North America for 2025. Read More
Maersk App now allows post-booking purchase of additional detention freetime, enhancing flexibility. Read More
ACD certificate mandatory for all container shipments to Yemen from February 1, 2025. Read More
Maersk announces review of Mauritius local charges, effective March 1, 2025. Read More
Global Factory Output – Overview
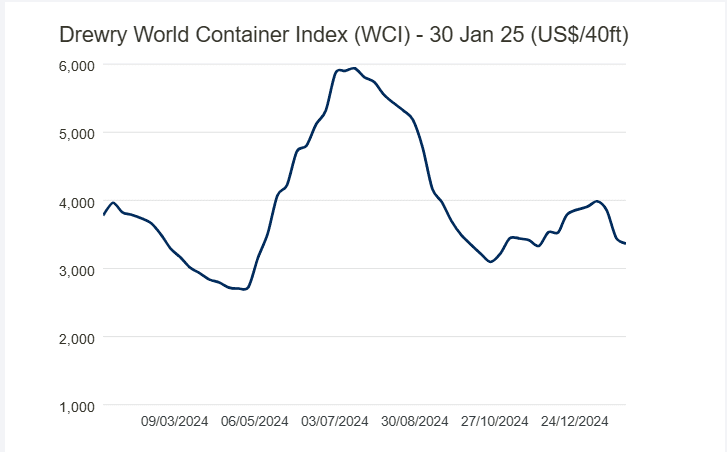
The World Container Index has reached $3,364 per 40ft container after a reduction of 2% at the end of January.
United States of America (USA)
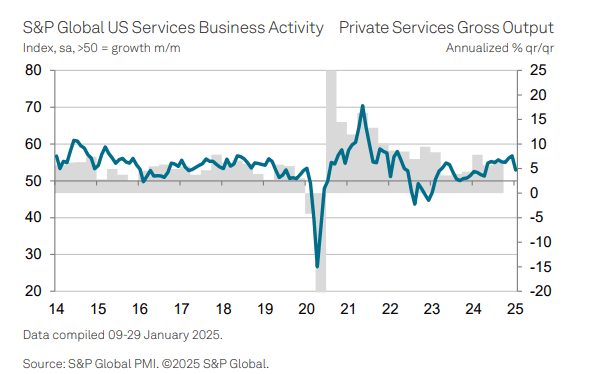
At the start of 2025, the service sector experienced a slowdown with activity levels not matching the robust gains of late 2024, signaling an annualized GDP growth rate of 1.6% for January, down from 2.4% in the previous quarter. Disruptions from adverse weather are partly blamed, but with a recent upturn in manufacturing and hiring, there’s potential for recovery in February. However, softer demand in sectors sensitive to interest rate changes and a slight decline in business optimism suggest cautious sentiments post-election, while increased hiring and price pressures may dampen hopes for rate cuts.
United Kingdom (UK)
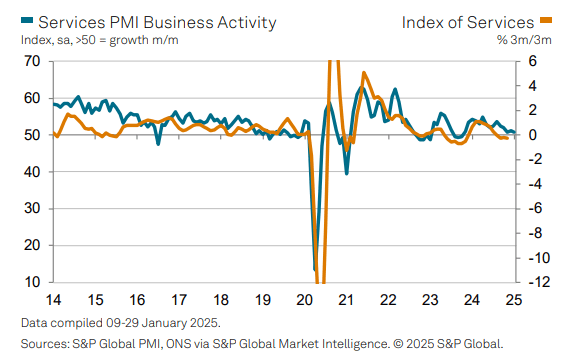
In January, UK service providers faced stagflation, with slight output increases and a sharp rise in input costs, driven by higher salaries and national insurance contributions. New business volumes declined, reflecting a downturn in economic outlook and risk aversion among clients. Business optimism reached its lowest since December 2022, leading to significant job cuts across the service sector, particularly in leisure and hospitality.
China
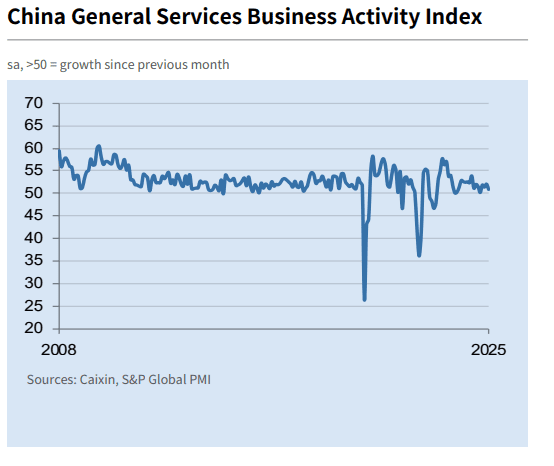
China’s services sector started 2025 with growth, though the pace slowed from December, marked by a drop in the Caixin Services Index to 51.0. Despite rising new business, including from abroad, softened demand led to job cuts—the fastest since April last year—due to better operational efficiency and minimal capacity pressure. Firms raised prices slightly due to increasing input costs but remained cautiously optimistic about future growth amid concerns over competitive and trade challenges.
United Arab Emirates (UAE)
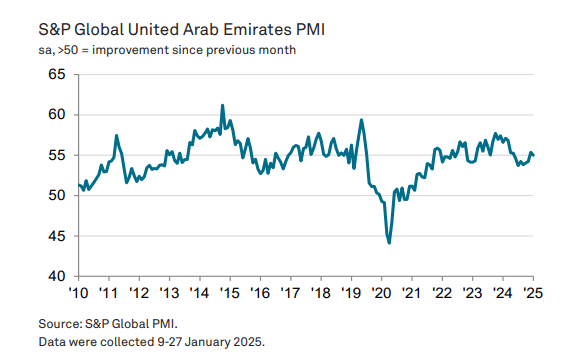
In January, the UAE’s non-oil private sector continued to perform well, with a slight drop from December’s nine-month high in the headline PMI. Despite robust expansions in activity and new business, along with lower input costs, business confidence reached its lowest since December 2022 due to intense competition and cash flow concerns from heavy backlogs. Employment growth remains low, and weak input resource availability is exacerbating capacity pressures as work-in-hand significantly increased.
Related Articles
March 2025 Global Trade & Logistics Market Update
Ramadan 2025: Road Restrictions and Their Impact on Logistics in Abu Dhabi With Ramadan 2025 approac
Monthly Update on the Global Logistics Market – February 2025
Major Shifts in Carrier Alliances Reshape Global Shipping Dynamics 2025 marks a pivotal year in the
January 2025 Supply Chain and Logistics Industry Outlook
Supply Chain Trends to Watch in 2025 In 2025, the supply chain industry is set to undergo significan






Post a comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.